
Breast Augmentation
Detailed Procedure Information
Breast augmentation, often referred to as augmentation mammaplasty, is a widely performed cosmetic surgery aimed at enhancing the size, shape, and symmetry of the breasts. This procedure can involve the insertion of silicone or saline implants, or in select cases, the transfer of fat harvested from other areas of the body. It remains one of the most sought-after aesthetic surgeries worldwide.
What Is Breast Augmentation?
At its core, breast augmentation is designed to improve breast volume and contour, addressing concerns such as underdeveloped breasts, irregular breast size, or loss of breast fullness due to aging, pregnancy, or weight changes. Whether you seek a subtle increase or a pronounced enhancement, the surgery is customizable to your unique desires and physiology.
Reasons to Consider Breast Augmentation
This surgery may be the ideal solution if you experience any of the following:
- Breasts that feel disproportionally small for your body frame.
- Asymmetry where one breast is noticeably smaller than the other.
- Loss of firmness and volume after pregnancy, breastfeeding, or significant weight loss.
- Desire to improve self-confidence and how clothes fit.
- Mild to moderate sagging potentially addressed with a combined breast lift.
Benefits of breast augmentation include improved breast size and shape, enhanced body proportion, correction of asymmetry, and boosted self-esteem.
Important Considerations Pre-Surgery
Prior to the procedure, it’s vital to have a consultation with an experienced plastic surgeon to assess your medical health and realistic expectations. Implants do not last a lifetime and may require replacement or removal in the future. Your surgeon may also discuss options such as combining augmentation with a breast lift for optimal results. The typical recovery spans one to two weeks. Additionally, there is a rare risk of Breast Implant Associated-Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL) that should be discussed carefully with your surgeon.
How Is Breast Augmentation Performed?
The procedure is commonly performed on an outpatient basis and involves either implants or fat transfer for breast volume enhancement.
Implant-Based Augmentation
The surgeon makes a discreet incision and creates a pocket either under the breast tissue or under the chest muscle to position the implant securely.
Fat Transfer Augmentation
If implants aren’t preferred, fat grafting can be an alternative. This involves liposuction to collect fat cells from areas such as the abdomen or thighs, which are then purified and strategically injected into the breasts. This method depends on sufficient fat availability and may require multiple treatments for optimal volume retention.
Breast Implant Placement Options
Implants can be positioned in one of two locations depending on individual anatomy and surgical goals:
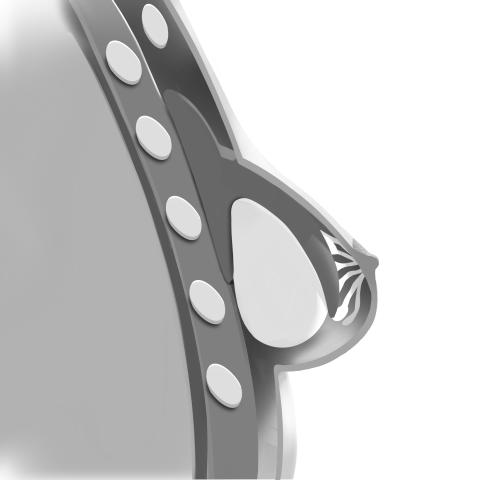
Submuscular Placement
The implant sits beneath the pectoral muscle, which can provide a more natural contour and potentially interfere less with breastfeeding and mammogram imaging. However, muscle flexing may cause slight implant movement.
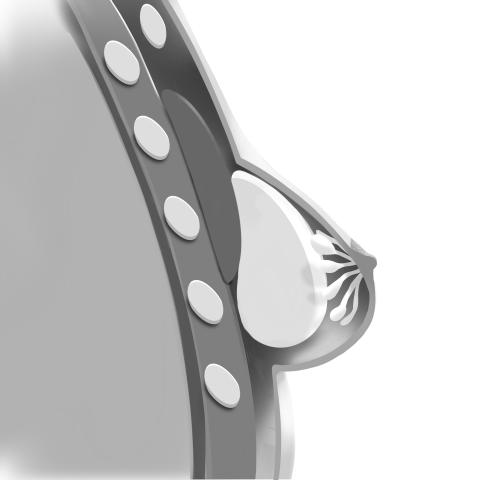
Subglandular Placement
The implant is placed over the pectoral muscle but beneath the breast tissue. This approach avoids muscle distortion with movement but may have a greater impact on mammogram visibility and breast-feeding.
Types of Breast Implants
Implant choice is personalized based on your anatomy, preferences, and surgeon’s recommendations. Common types include:
- Saline Implants: Filled with sterile saltwater, either prefilled or filled during surgery to allow size adjustments.
- Structured Saline Implants: Contain an internal structure mimicking the feel of silicone while maintaining saline fill.
- Silicone Gel Implants: Filled with soft silicone gel, these offer a more natural feel and come in various shapes and firmness levels.
- Cohesive Silicone Gel (“Gummy Bear”) Implants: Made with highly cohesive silicone gel that maintains shape and firmness better than traditional silicone implants.
Selecting a Surgeon
Finding a Qualified Surgeon You Trust
Choosing the right surgeon is crucial for a safe procedure and satisfying results. When searching for your aesthetic plastic surgeon, consider the following:
- Board certification and relevant training in plastic surgery.
- Demonstrated experience in breast augmentation surgery.
- Reviewing the surgeon’s portfolio of before and after photos.
- Your personal acceptance and comfort with the surgeon.
- Membership in recognized professional societies such as The Aesthetic Society.
Take advantage of resources like guides on finding qualified surgeons and tools to locate specialists near you.
What to Expect During Your Consultation
Consultations typically involve a thorough discussion about your goals and a detailed physical examination, including breast measurements and photographs for records. Your surgeon will explore:
- Your current breast shape, size, and skin quality.
- Your desired breast volume and aesthetics.
- Nipple and areola positioning.
- Your full medical history, including previous surgeries, current medications, allergies, family breast cancer history, and lifestyle factors like smoking.
The consultation also ensures you understand realistic outcomes and whether a breast lift or alternative procedure might be beneficial.
Questions to Ask Your Surgeon
Be prepared to actively engage by asking important questions such as:
- Am I a suitable candidate for breast augmentation?
- Do you recommend implants or fat transfer?
- What implant type and placement would best suit me?
- What anesthesia will be administered?
- What can I expect during recovery and potential complications?
- How will my breasts look over time and after pregnancy or breastfeeding?
- What are your credentials and experience with this procedure?
Further guidance on inquiry can be found in our comprehensive question list for your surgeon.
Preparing for your Procedure
Essential Preoperative Steps
Your surgeon will provide detailed instructions tailored to your health status and surgical plan. General recommendations include:
- Ceasing tobacco use to improve healing.
- Avoiding certain medications and supplements that can increase bleeding risk, such as aspirin and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Ensuring adequate hydration before and after surgery.
- Wearing a special bra preoperatively to prepare the breast tissue for fat grafting if applicable.
Imaging and Testing
Women over 40 may be advised to have a baseline mammogram prior to surgery, with follow-up imaging after healing to monitor breast health.
Day of Surgery Expectations
- The procedure will commonly be done at an accredited hospital or ambulatory surgical center under general anesthesia or sedation.
- Surgery usually lasts between one to two hours, potentially longer if combined with other procedures.
- Your vital signs and oxygen levels will be carefully monitored throughout.
- Postoperative recovery will take place in a designated area with professional care until you are stable for discharge.
Implant and Fat Transfer Specific Details
For implants, sterile bandages or a surgical support bra will be applied, and drains may be used temporarily. Fat transfer procedures involve a two-step approach with liposuction followed by injection, necessitating compression garments on both donor and recipient sites.
Aftercare & Recovery
Recovery Timeline
Typical recuperation from breast augmentation ranges from one to two weeks, after which you may gradually resume normal routines as advised.
Postoperative Experiences
- Initial bandaging or support garments will help reduce swelling and support healing.
- Pain and tenderness peak during the first two days but should diminish steadily; medication will be prescribed as needed.
- Swelling, tightness, and sensitivity are common and generally improve within weeks.
- Arm mobility may be temporarily limited due to discomfort.
- Sleeping positioned on your back at a slight incline helps facilitate healing and reduce swelling.
- Early ambulation is critical to prevent blood clots—short walks every few hours are recommended.
- Heavy lifting, bending, or strenuous activity should be avoided to prevent complications.
First Week Recovery Details
- The chest may feel stiff or sore; report severe pain to your surgeon immediately.
- Surgical dressings and drains are typically removed during the first week, and a support bra worn as instructed.
- Showering is usually allowed within days, depending on incisional healing.
- External sutures may be removed at around one week.
- Many patients can return to sedentary work within days to a week.
- Avoid upper body exertion that increases pain or swelling.
Longer-Term Recovery
- Restrict vigorous physical activity for at least several weeks post-surgery.
- Sexual activity should be paused for around two weeks, resuming gently.
- Routine breast examinations and mammograms should continue as recommended.
- Breast self-examinations remain an important ongoing health practice.
Results
Longevity and Maintenance of Results
Breast implant results typically last many years but are not considered permanent and may require replacement. The longevity depends on implant type, surgical technique, and individual factors.
Fat transfer augmentation results tend to be long-lasting but may show gradual volume loss and sagging over time.
Long-term breast appearance can be influenced by:
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Aging and hormonal changes
- Weight fluctuations
- Gravity’s effects
Visualizing before and after images can assist in forming realistic expectations on outcomes.
Postoperative Considerations
Follow-up visits with your plastic surgeon are critical to monitor implant integrity and breast health. Should dissatisfaction or complications arise, options such as breast revision or breast lift procedures may be discussed to restore optimal aesthetics.
Incisions and Scars
Types of Surgical Incisions for Breast Augmentation
The incision approach depends on implant choice, size, and surgical strategy:
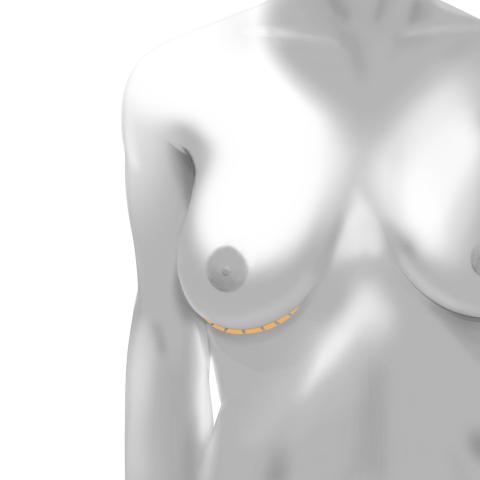
Inframammary Incision
This is made along the crease beneath the breast. It offers the most direct implant access, especially preferred for larger implants. The scar is well concealed within the breast fold.
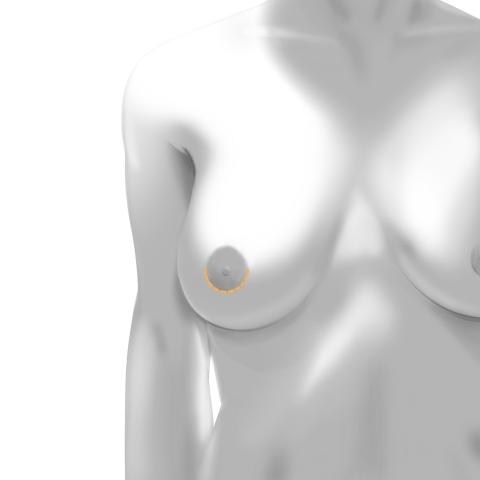
Periareolar Incision
Placed around the lower edge of the areola. This method allows good access for smaller implants and generally leaves minimal visible scarring. It may carry a slightly higher risk of capsular contracture.
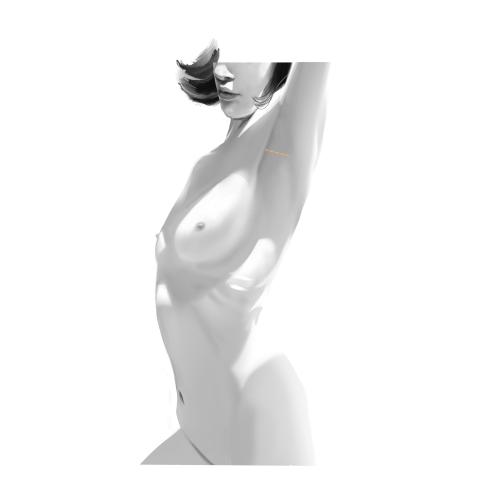
Transaxillary Incision
Made near the armpit crease. Scarring is hidden in the underarm area. This technique requires more tissue manipulation and carries some risk of nerve impact but avoids breast scars.

Transumbilical Incision
An incision within the navel is sometimes used with saline implants. It leaves no breast scars but offers limited control and may distort the belly button appearance. This approach is less common.
Scar Appearance and Healing
All incisions will result in permanent scars; however, expert technique ensures scars are minimized and positioned in inconspicuous locations. Scars typically fade significantly over time with proper care. Healing quality depends on surgical method, patient biology, and adherence to postoperative instructions such as maintaining nutrition, avoiding smoking, and infection prevention.
Safety Considerations
Potential Risks and Complications
Breast augmentation is generally safe when performed by a qualified surgeon; however, like all surgeries, it carries potential risks. Common surgical risks include:
- Adverse reactions to anesthesia
- Hematoma or seroma (blood/fluid collection requiring drainage)
- Infection and associated bleeding
- Changes in breast or nipple sensation
- Visible scarring variations
- Allergic reactions
- Damage to surrounding tissues
- Unsatisfactory aesthetic results possibly needing revision surgery
Risks Specific to Breast Implants
- Capsular contracture (scar tissue tightens around the implant)
- Implant rupture or leakage
- Interference with mammogram imaging
- Rare but serious Breast Implant Associated-Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL)
Regular monitoring with your surgeon is essential to detect and address potential concerns early.
Are Breast Implants Safe?
Ongoing advancements in surgery and implant technology have improved safety profiles. Regulatory bodies like the FDA affirm that breast implants approved for use have passed rigorous safety standards. Importantly, silicone gel implants have been extensively studied without proven links to systemic disease.
The rare BIA-ALCL lymphoma is treatable and has prompted safety guidelines emphasizing patient awareness and timely surgeon evaluation if symptoms such as unexplained swelling or changes in breast shape occur.
Women with implants should maintain routine breast cancer screening, utilizing skilled radiologists trained to work with augmented breasts. Supplemental imaging like ultrasound or MRI may sometimes be required for effective surveillance.
Associated Costs
Understanding the Costs of Breast Augmentation
The total expense of breast augmentation can fluctuate based on factors such as your chosen surgeon’s expertise, location, type of implants or fat transfer method, facility fees, anesthesia, and postoperative care. Costs vary widely, so it is advised to discuss the estimated financial investment during your consultation.
Factors Influencing Implant Costs
- Saline implants generally have lower cost compared to silicone.
- Structured saline and cohesive gel (gummy bear) implants carry higher prices due to advanced design.
Insurance Coverage
Breast augmentation for cosmetic reasons is considered elective and typically not covered by insurance. Some patients may benefit from financing options offered by providers to assist with payment plans.
Choosing Quality over Cost
While affordability is important, prioritize selecting a board-certified plastic surgeon who prioritizes your safety and outcomes over lower fees. Fully informed decision-making and choosing a qualified specialist helps ensure optimal and lasting results with fewer complications.
Learn more about the quality standards upheld by our member surgeons at The Aesthetic Society.

