Eyelead Surgery
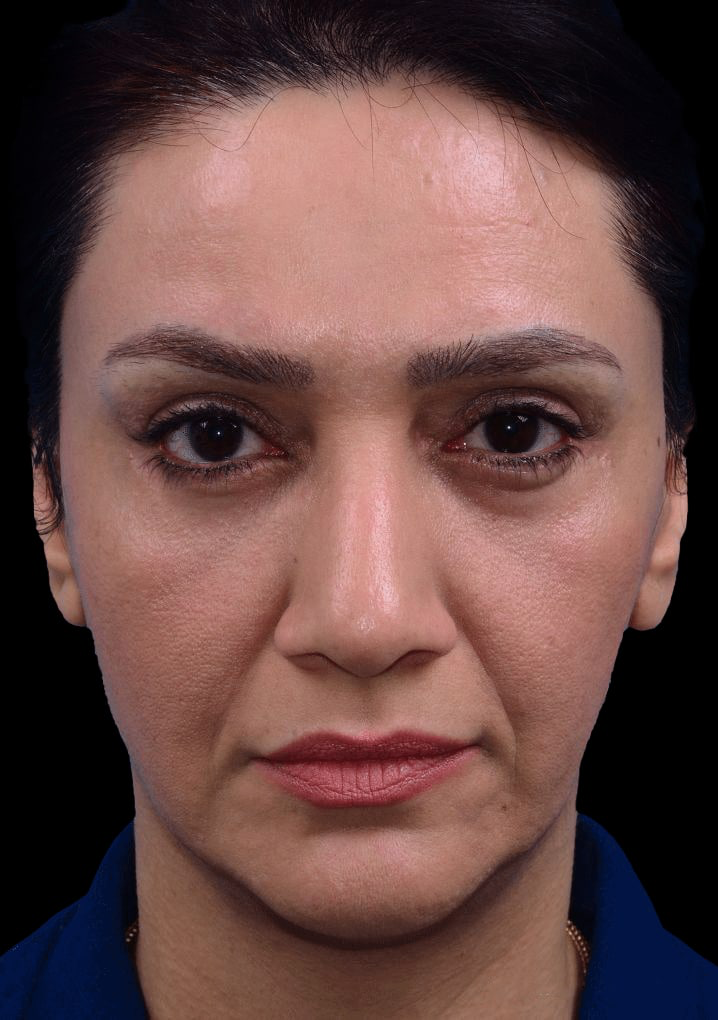
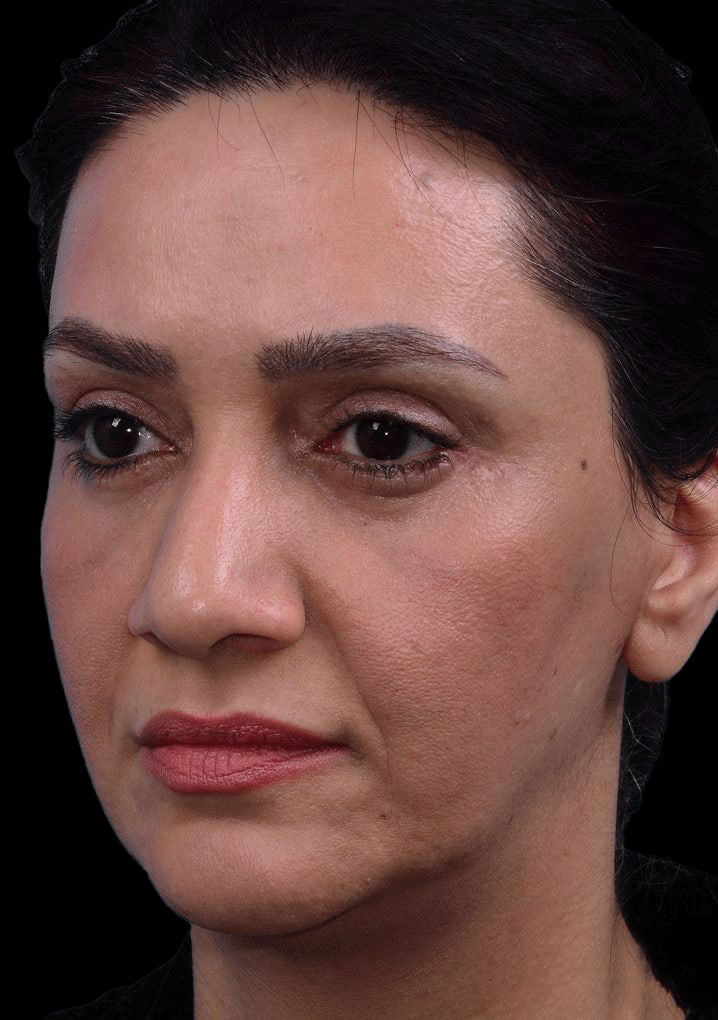
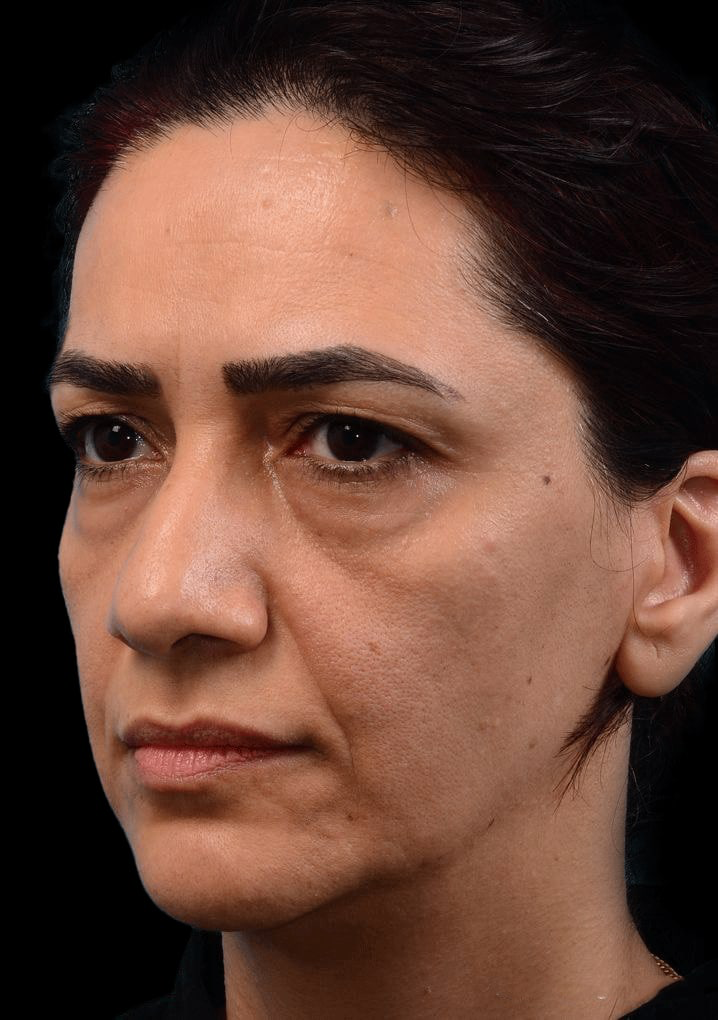
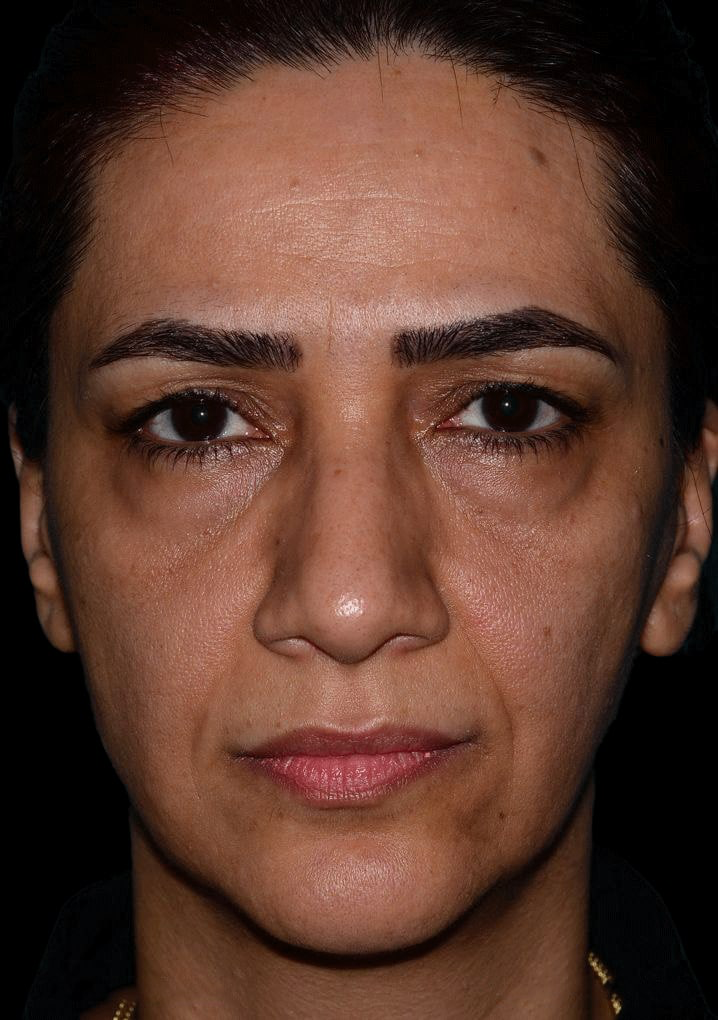

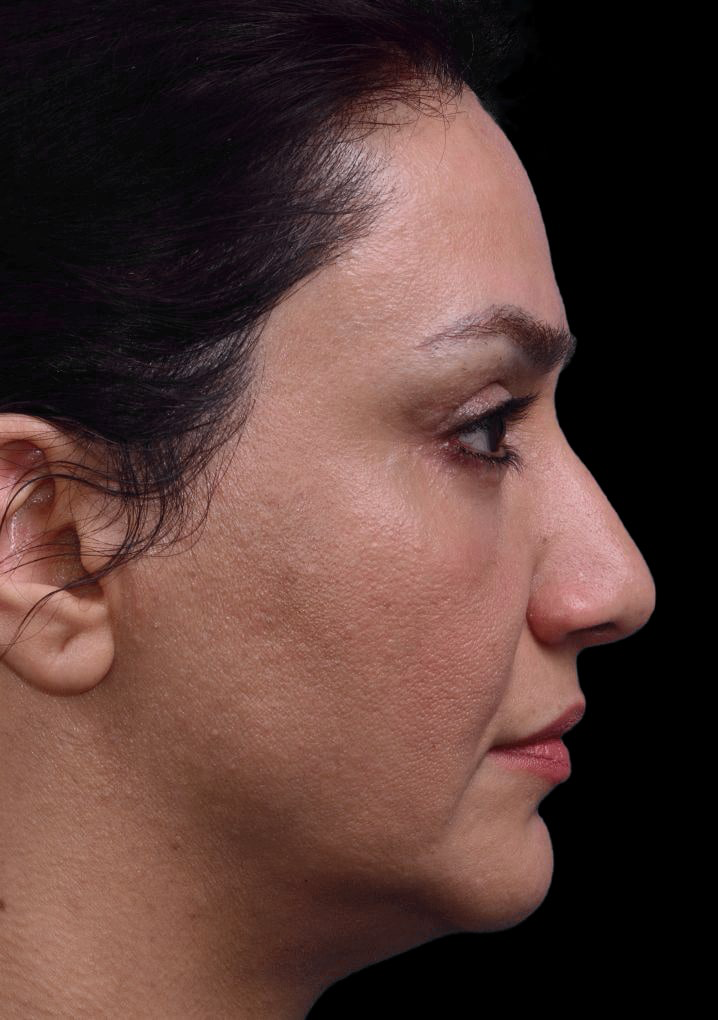
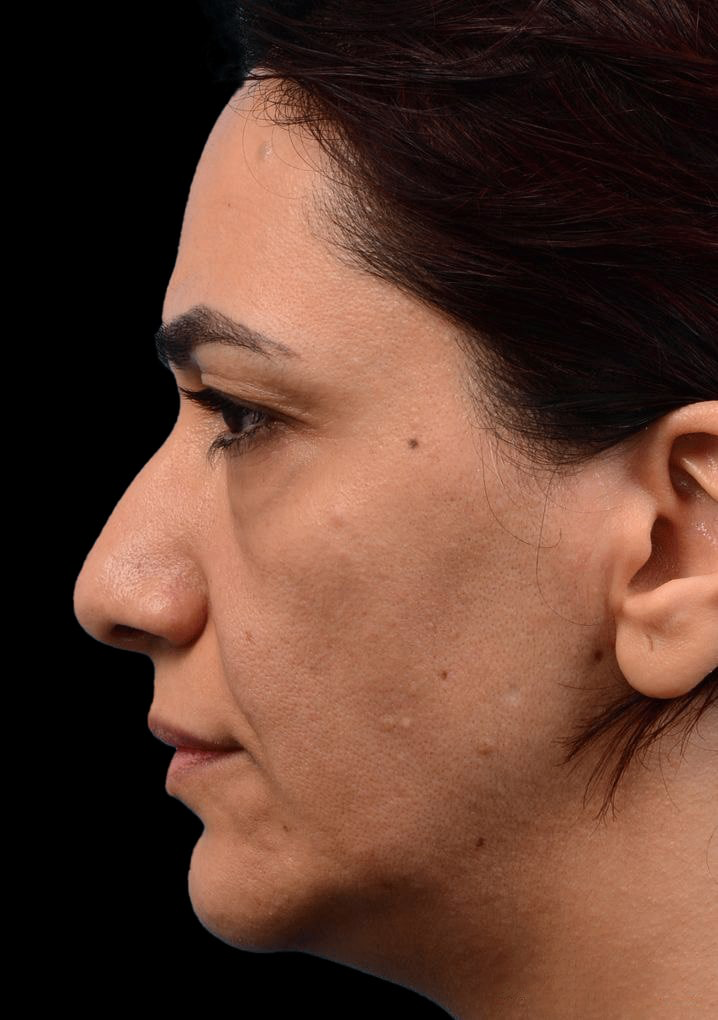


Eyelid Surgery
This summary covers blepharoplasty: what it is, who it’s for, risks, procedure, and results. Headings and essential points only.
What Is Eyelid Surgery?
- Surgical procedure to improve the appearance of the upper and/or lower eyelids.
- Treats loose or sagging skin, fat deposits, bags under the eyes, lower eyelid wrinkles, and drooping lower lids.
- Can also correct functional concerns like impaired vision due to excess skin.
What Eyelid Surgery Can Treat
- Loose sagging skin creating folds on the upper eyelid.
- Puffiness from fatty deposits in eyelids.
- Bags under the eyes.
- Lower eyelids drooping, revealing white area below the iris.
- Fine wrinkles and excess skin of lower eyelid.
Candidates
- Good physical health with no conditions that impair healing.
- Realistic expectations about what eyelid surgery can achieve.
- Non-smokers or willing to stop; skin condition suitable.
Cost
- Cost depends on whether upper, lower, or both eyelids are treated, plus complexity.
- Additional expenses include anesthesia, facility fees, and post-operative care.
Consultation
- Discuss aesthetic goals and any functional issues (e.g. vision obstruction).
- Review medical history, medications, previous eye surgeries.
- Assess eyelid anatomy, skin laxity, fat deposits, and general facial features.
Questions to Ask
- Which eyelids will be treated (upper, lower, or both)?
- What surgical technique will be used?
- What is the expected recovery time and aftercare?
- What are the specific risks (vision, scarring, dryness)?
- What results are realistic in my situation?
Risks and Safety
- Bleeding, infection, poor wound healing.
- Temporary or permanent changes in skin sensation.
- Excessive dryness or irritation of eyes.
- Visible scarring depending on incision location.
- Asymmetry or uneven result.
- Possible need for revision if complications or undesired outcome.
Preparation
- Medical evaluation, lab tests if required.
- Avoid medications or supplements that increase bleeding risk.
- Stop smoking in advance.
- Arrange someone to help during early recovery.
Procedure Steps
Anesthesia
- Local anesthesia, sometimes with sedation; in other cases general anesthesia as needed.
Incision & Technique
- Incisions usually made in natural creases of upper eyelids or just below the lash line for lower lids.
- Excess skin removed; fat may be repositioned or removed; underlying support tightened if needed.
Closure
- Sutures or adhesives used to close incisions; sometimes removable, sometimes dissolvable.
- Incision placement aimed to minimize visible scarring.
Recovery
- Swelling and bruising expected after surgery; may last several days.
- Cold compresses, proper head elevation help reduce swelling.
- Avoid strenuous activity, bending or lifting in early post-op period.
- Follow-up appointments to remove sutures (if required) and monitor healing.
Results
- More youthful, rested appearance around the eyes.
- Reduced bags, folds, and excess skin contributing to heaviness.
- Improvement in vision if upper eyelid skin was obstructing sight.
- Scars usually fade over time, largely hidden in natural eyelid creases.
Choosing a Plastic Surgeon
- Board-certified plastic surgeon with experience in eyelid surgery.
- Use of accredited surgical facility and proper aftercare support.
- Review before & after photos of similar cases; ensure clear communication of expectations.

